 |
Hands-On-Physics
HEAT & TEMPERATURE
|
Messing
Around
|
- Calibration -
|
To get accurate measurements from a sensor, you have to calibrate. In this
activity, you calibrate one of the sensors for later use. Calibrating your
sensors lets you convert your readings into temperature. For instance, calibration
would let you convert the resistance readings from a thermistor into degrees.
Your goal is to come up with a way of converting "raw data", the
readings on your meter, to temperature. The following sketch suggests one
way. Calibration always involves two measuring devices. To calibrate, you
compare readings from a standard device to the readings of the sensor you
are calibrating.
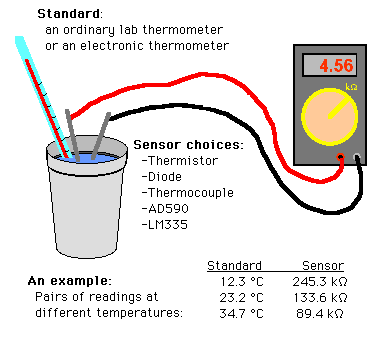
Figure M6
Scheme for Calibration of a Sensor
In the calibration curve shown below, five data points, indicated by
crosses, have been taken across a range of temperatures. Then a smooth curve,
shown in green, was fit to these data. Later, if you measure a resistance,
a, shown in blue, then this reading can be converted to a temperature, b,
shown in red.
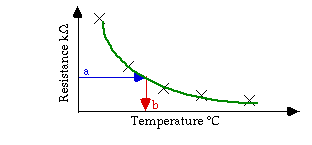
Figure M7
Calibration cure
Steps in Calibration
- Pick the standard you are going to use for measuring temperature:
You can use a good lab thermometer, an electronic thermometer, or one of
the integrated circuits, the AD590 or the LM335. Next, pick the sensor you
will callibratep;it can be a thermistor, diode, thermocouple, or one
of the integrated circuits. Each sensor may be a bit different from the
next, so put a tag on the sensor you calibrate so you can identify it later.
- Think and plan:
What is your goal? Over what range of temperatures do you need accurate
calibration? How can you keep errors to a minimum? How much data will you
need? Write your group's questions and answers in a lab notebook.
- Take Data:
Take pairs of readings at each temperature. Each pair consists of a temperature
according to your standard and the raw data from your sensor. Take these
carefully when the temperatures of the standard and sensor are exactly the
same. Be as accurate as possible. Take enough pairs to give you an accurate
graph over the entire range that you will need.
- Make a Calibration Curve:
Generate a graph like the one above using your data. Use a graphing
spreadsheet if one is available. Make it clear what data you took
and then draw a smooth curve through these data.
- Use Your Calibration Curve:
Measure some new temperatures and use the graph to convert your meter readings
into temperature. Measure your body temperature, the temperature of a coin
in the sun, the temperature of a light bulb.
- Fit Your Data:
Using a hand-drawn graph to convert readings to temperatures can introduce
errors. A better way is to use the computer to graph and fit your data.
You can do this with a graph made by a
spreadsheet
using algebra.
Previous Page ||
Up a Level ||
Index ||
Next Page